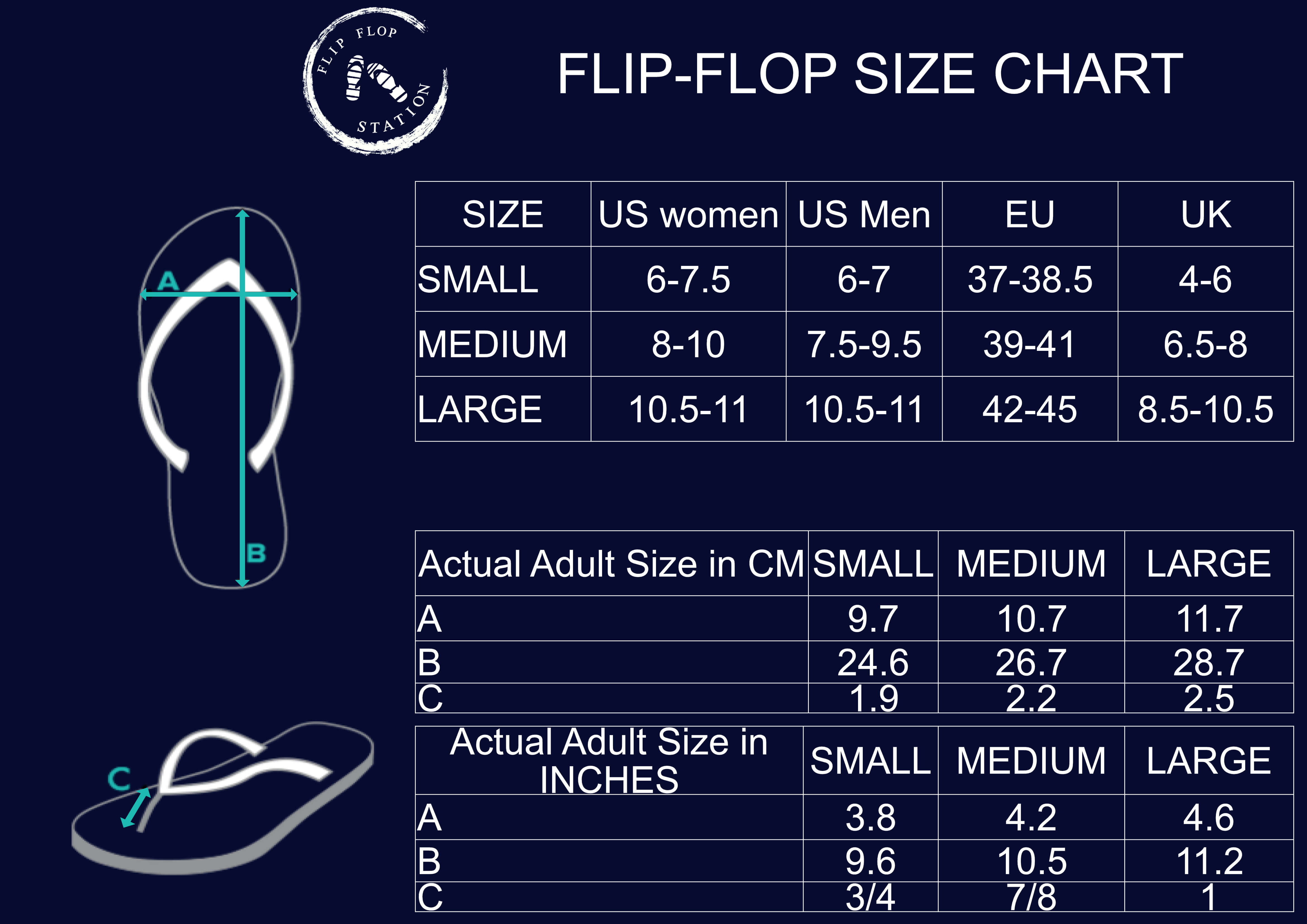



Estimated Delivery:
More information
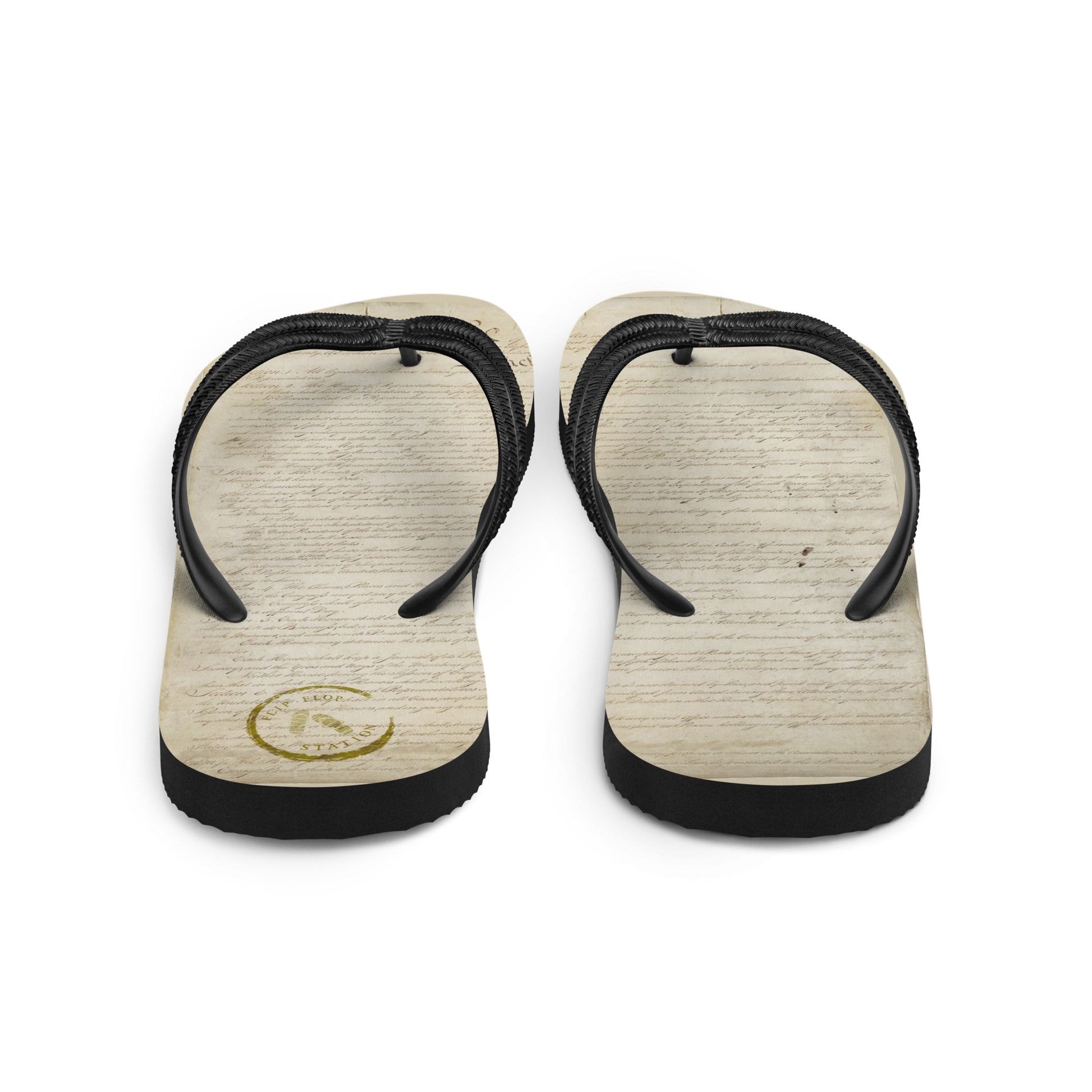
On September 17th, 1787, one of the most significant events in American history occurred: the signing of the United States Constitution in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania.
The United States Constitution is the supreme law of the United States and serves as the foundation of the country's government. The Constitutional Convention, which began in May 1787 and lasted throughout the summer, was convened to address the weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation, the nation's first governing document. Delegates from 12 of the 13 states (Rhode Island did not send representatives) gathered to draft a new constitution that would create a stronger federal government while still preserving the rights of individual states and citizens.
After months of debate, compromise, and negotiation, the delegates reached an agreement on the Constitution's text. On September 17th, 1787, 39 delegates signed the final version of the Constitution, including notable figures like George Washington, Benjamin Franklin, Alexander Hamilton, and James Madison. This historic event marked the birth of the U.S. Constitution.
The Constitution established a system of government with three separate branches—executive, legislative, and judicial—to ensure a system of checks and balances. It outlined the powers and responsibilities of each branch and defined the relationship between the federal government and the states. The Constitution also included the Bill of Rights, the first ten amendments, which guaranteed individual freedoms and rights.
The signing of the U.S. Constitution was a pivotal moment in history, as it laid the groundwork for the establishment of the United States as a federal republic. It has endured for over two centuries, making it one of the oldest written national constitutions still in use. September 17th is now celebrated as Constitution Day in the United States, a day to reflect on the principles and ideals that have shaped the nation's government and society.
The United States Constitution is the supreme law of the United States and serves as the foundation of the country's government. The Constitutional Convention, which began in May 1787 and lasted throughout the summer, was convened to address the weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation, the nation's first governing document. Delegates from 12 of the 13 states (Rhode Island did not send representatives) gathered to draft a new constitution that would create a stronger federal government while still preserving the rights of individual states and citizens.
After months of debate, compromise, and negotiation, the delegates reached an agreement on the Constitution's text. On September 17th, 1787, 39 delegates signed the final version of the Constitution, including notable figures like George Washington, Benjamin Franklin, Alexander Hamilton, and James Madison. This historic event marked the birth of the U.S. Constitution.
The Constitution established a system of government with three separate branches—executive, legislative, and judicial—to ensure a system of checks and balances. It outlined the powers and responsibilities of each branch and defined the relationship between the federal government and the states. The Constitution also included the Bill of Rights, the first ten amendments, which guaranteed individual freedoms and rights.
The signing of the U.S. Constitution was a pivotal moment in history, as it laid the groundwork for the establishment of the United States as a federal republic. It has endured for over two centuries, making it one of the oldest written national constitutions still in use. September 17th is now celebrated as Constitution Day in the United States, a day to reflect on the principles and ideals that have shaped the nation's government and society.